How Radiographic Testing Works: Basic Principles
To fully understand radiographic testing, it is important to be generally familiar with radiation and how it interacts with and affects materials at the atomic level.
)
Discover the advantages of the radiographic testing (RT) method, understand the basic principles of RT, and explore the variety of techniques for applying this highly adaptable method in nondestructive testing across industries.
This method is highly beneficial to numerous industries due to its ability to find subsurface flaws that may lead to failure of a component in service. However, it does come with inherent safety risks, as radiation can be dangerous to humans without the proper precautions.
A skilled NDT specialist applies different RT techniques depending on the nature of the inspection while adhering to proper regulations that protect both themselves and the public.
The primary objectives of RT in industrial applications include:
Locating internal defects: RT can easily locate internal structural discontinuities using visual comparison with known geometric features of the object being inspected, and it creates a visual rendition of internal voids and fabrication errors that is easy to interpret.
Volumetric examination: RT is considered by many to be the most universal approach to volumetric examination, which examines the internal integrity of the object being inspected.
Creating a record: RT inspections produce a permanent record of the inspection—including evidence of the sensitivity of the test when image quality indicators (IQIs) are used—and can provide a digital record of the object being inspected for subsequent display.
The ability of RT to evaluate the internal structure of an object without damaging it makes it invaluable in many industries.RT is a versatile method applicable in many industries, including manufacturing, aerospace, oil and gas, and more.
Modern advances make RT a method of great importance for continued development of automation and artificial intelligence. With the continued growth of additive manufacturing, radiographic inspection will find a home as one of the only ways to gather information regarding complex internal components that are otherwise inaccessible.”
To fully understand radiographic testing, it is important to be generally familiar with radiation and how it interacts with and affects materials at the atomic level.
Understanding the fundamental building blocks of matter is crucial for comprehending the principles behind RT. Atoms, the basic units of matter, play a key role in how materials interact with radiation.
By exploring the structure of atoms, elements, isotopes, and radioisotopes, we can better understand how RT detects and analyzes defects within materials.
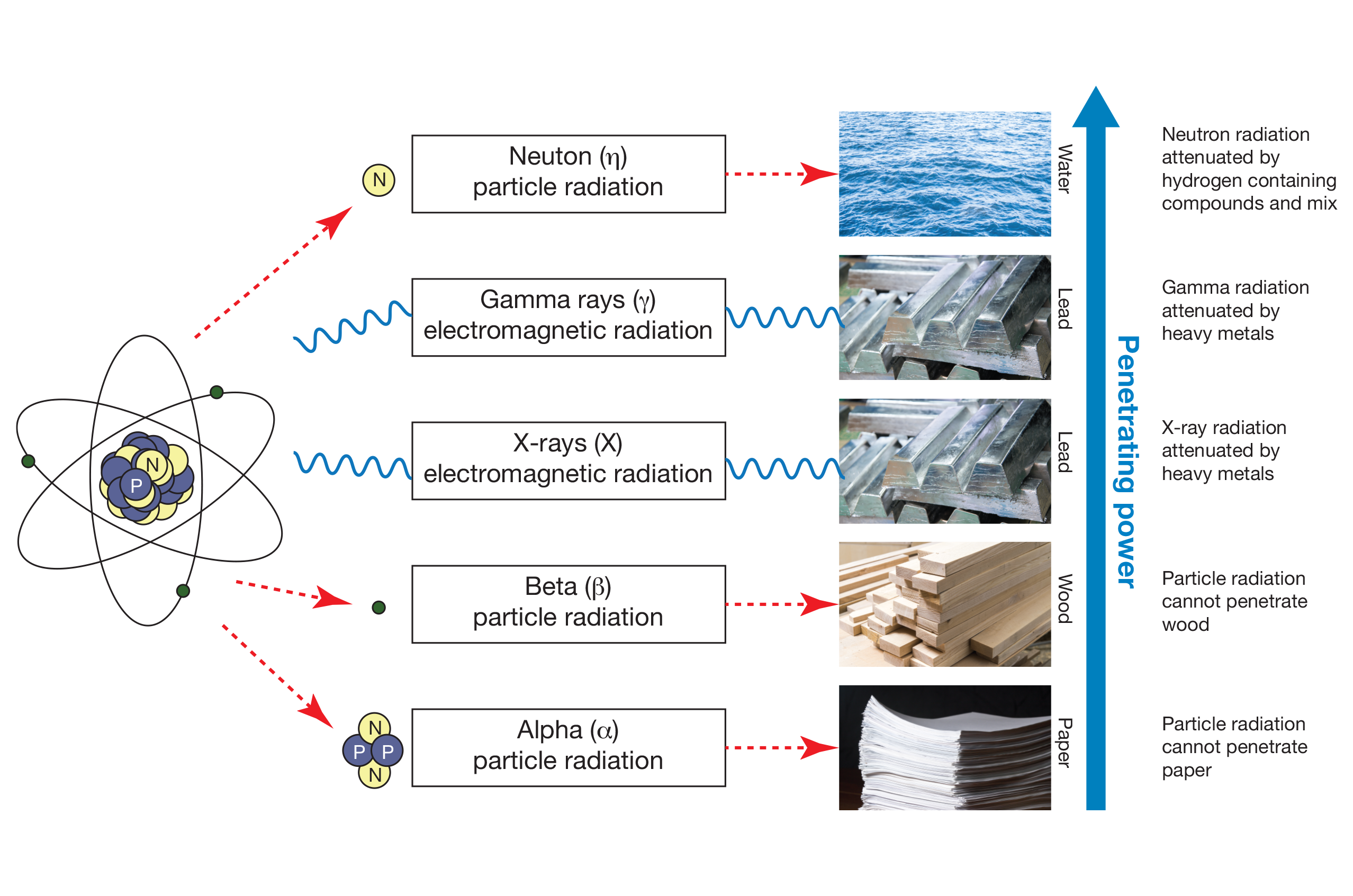
When atoms become radioactive, they can emit different types of radiation that each have different ways of interacting with materials. Gamma and X-ray radiation are used in radiographic testing due to their high energy and ability to penetrate through many materials.
X-ray Radiation: X-rays are generated from a tube head powered by an electrical current. High-speed electrons are abruptly halted by a tungsten target, converting their kinetic energy into heat and X-ray photons. Unlike gamma radiation, X-rays have controls that allow for adjustment in both quantity and energy intensity.
Gamma Ray Radiation: Energy photons (packets of electromagnetic radiation) are emitted from the nucleus of unstable isotopes. Gamma waves penetrate most matter but can be stopped by a dense (high atomic number) material such as lead, depleted uranium, and very thick steel. It is most applicable in remote areas where electrical power to produce X-rays is not practical.
)
Radiographic Testing (RT) employs a variety of techniques to detect and measure discontinuities in materials. These techniques can be categorized based on how the ultrasonic waves are introduced into the material and the specific modes and advanced methods used to enhance flaw detection and measurement.
There are four primary methods used.
ASNT certifications enable you to become a qualified Level II or Level III in RT or obtain your industrial radiography radiation safety personnel (IRRSP) certification.
What Certification Is Right for Me?Radiographic Testing (RT) can be used on a wide range of materials, including metals, composites, and concrete. Its ability to offer detailed internal imaging, high penetration capability, and permanent records makes it invaluable for ensuring the integrity and safety of critical components and structures.
These characteristics make it an important nondestructive testing (NDT) method that’s widely used across a range of industries.
In the oil and gas industry, NDT professionals use RT responsible for inspecting pipelines, storage tanks, and offshore structures for defects and corrosion to ensure compliance with safety standards and prevent environmental hazards. RT is crucial in ensuring the safety and integrity of nuclear power plants.
Learn More
RT is used in the aviation industry to ensure the structural integrity of aircraft components, engines, and airframes. Professionals in aviation NDT conduct inspections using techniques such as X-ray inspection and computed tomography to check critical components and ensure they meet stringent safety standards.
Learn More
RT is vital for inspecting critical components for boats and submarines, ensuring castings made with copper-nickel alloys are free of conditions such as shrinkage or porosity.
Learn More
RT is used to ensure the quality and reliability of automotive components such as engine parts, chassis, and welds, to detect defects and deviations from specifications. With new technologies like 3D printing and additive manufacturing, NDT is crucial for quality control and ensuring dimensional accuracy and material integrity.
Learn More
In infrastructure and construction, NDT practitioners use RT is used to inspect structural steel, welds, and other critical components during construction and maintenance to detect flaws such as cracks, voids, and inclusions.
Learn More
ASNT offers both members and nonmembers learning opportunities and resources for NDT specialists certifying in and using UT.
Members get discounts on courses, events, and resources. Join and save!
Become a member today!
